Ground Truth is the Alpha and Omega
Release 1.7.1
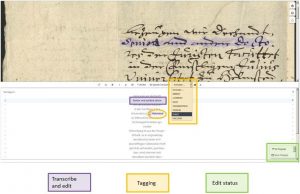
Ground Truth (GT) is the basis for the creation of HTR models. It is simply a typewritten copy of the historical manuscript, a classic literal or diplomatic transcription that is 100% correct – plainly “Groundt Truth”.
Any mistake in this training material will cause “the machine” to learn – among many correct things – something wrong. That’s why quality management is so important when creating GT. But don’t panic, not every mistake in the GT has devastating consequences. It simply must not be repeated too often; otherwise it becomes “chronic” for the model.
In order to ensure the quality of the GT within our project, we have set up a few fixed transcription guidelines, as you know them from edition projects. It is worthwhile to strive for a literal, character-accurate transcription. Regulations of any kind must be avoided; e.g. normalizations, such as the vocal or consonant usage of “u” and “v” or the encoding of complex abbreviations.
If the material contains only one or two different handwritings, about 100 pages of transcribed text are sufficient for a first training session. This creates a basic model that can be used for further work. In our experience, the number of languages used in the text is irrelevant, since the HTR models usually work without dictionaries.
In addition to conventional transcription, Ground Truth can also be created semi-automatically. Transkribus offers a special tool – Text2Image – which is presented in another post.